

Data Center Cooling:The History And The Future
It's no secret that data centers are one of the largest consumers of electricity worldwide and the industry is experiencing a significant increase in power density and hence a greater cooling challenge these years. As a result, the cooling systems continue to evolve as the rack densities continue to grow. This essay will focus on the history as well as the future of data center cooling system.
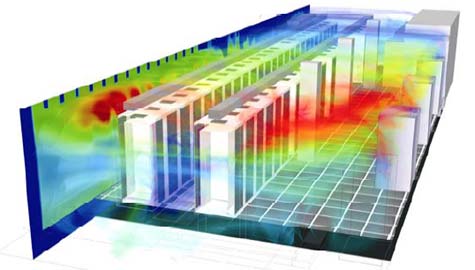
Raised floor systems
In the past 20 years, computer rooms and data centers have used raised floor systems to deliver cold air to servers. There are holes for ventilation on the floor where the server is placed. The cold air from CRAC and computer room air handler (CRAH) units is compressed into space under the raised floor and then flows through the perforated tiles to the main space in front of the server. After passing through the server, the heated air returned to the CRAC/CRAH to be cooled, usually after mixing with the cold air.
This arrangement were sufficient to overcome the heat dissipation from the servers in those times when data centers were primarily occupied by low-density IT equipment. Therefore it has been a popular cooling method for the past few decades despite its low efficiency and uneven cooling, .
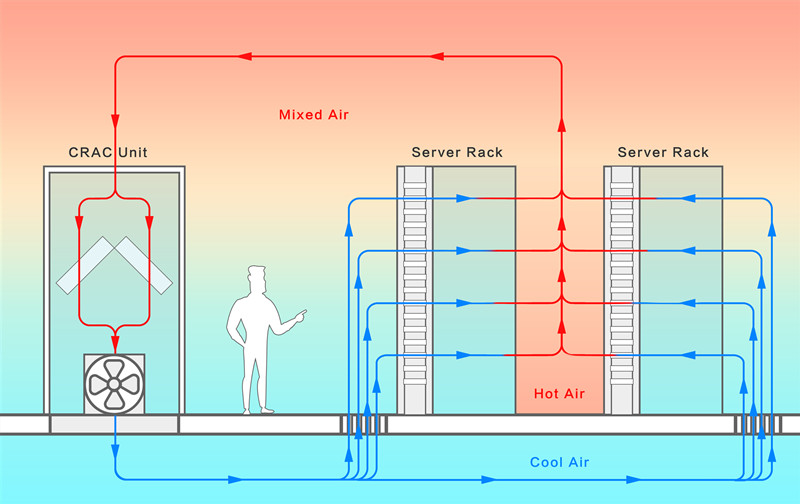
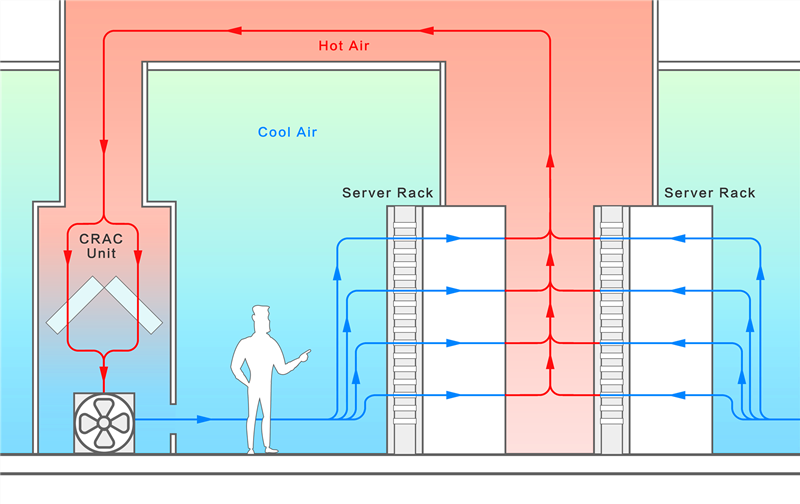
Hot and cold aisle containment layouts
Around 2005, data center experts and operators tested the idea of containment. They added physical barriers to separate the cold airflow from the server inlet from the hot airflow from the server. Avoiding mixing cold air supply and hot exhaust can greatly improve cooling efficiency and achieve energy saving.
Closed coupled cooling
In recent years as the power densities per rack have trended upward to 20 kW, CRAC units and hot and cold aisle containment may not provide adequate cooling. To address these situation, data center cooling vendors developed closed coupled cooling technology(CCC). The goal of CCC is to bring heat transfer closest to its source: the equipment rack. By moving the air conditioner closer to the equipment rack it enable energy-saving. What's more it can fix hot spots. With the combination of a Cold Aisle/Hot Aisle arrangement,the technology can have greater efficiency.

Closed coupled cooling technology includes in-row, in-rack, in-room, above–rack, and etc.
In-Row Air Conditioners: They are installed inside the rack rows. Air flows generally follow short and linear paths, reducing, in this way, the necessary power needed to start up the fans and increasing the energy efficiency.
In-Rack Cooling:the rack-based airflow paths are even shorter and exactly defined, so that airflows are totally immune to any installation variation or room constraints. It is the most flexible, fastest to implement, and achieves extreme density, but with additional expense.
Liquid-cooling solution
Another raising cooling method is the chip liquid cooling solution. When your rack densities reach as high as 100 kW per rack, you can give it a try. It is expensive but more efficient because water transfers heat more efficiently than air and it is environmentally friendly. Google had announced that they are using liquid cooling in their data centers in 2018 and Facebook used seawater to cool one of their data centers.
The future trends of cooling your data center
Air-based cooling systems and liquid cooling will continue reshaping what cooling means for the data center sector. “High-performance computing is likely to use liquid cooling, while enterprise data centers and Internet data centers (such as Microsoft's data centers) will continue to use air-cooled cooling methods.” Said Belady, a former Engineer of Hewlett-Packard Company.
